Bird's Eye View Transformation
May 07, 2017
3 mins read
Introduction
Parallel lines appear to converge on images from a front facing camera due to perspective. In order to keep parallel lines parallel for photogrammetry a bird’s eye view transformation should be applied. The post describes how to transform images for lane lines detection.
What transformation to use
Here it is a sample image to experiment with:
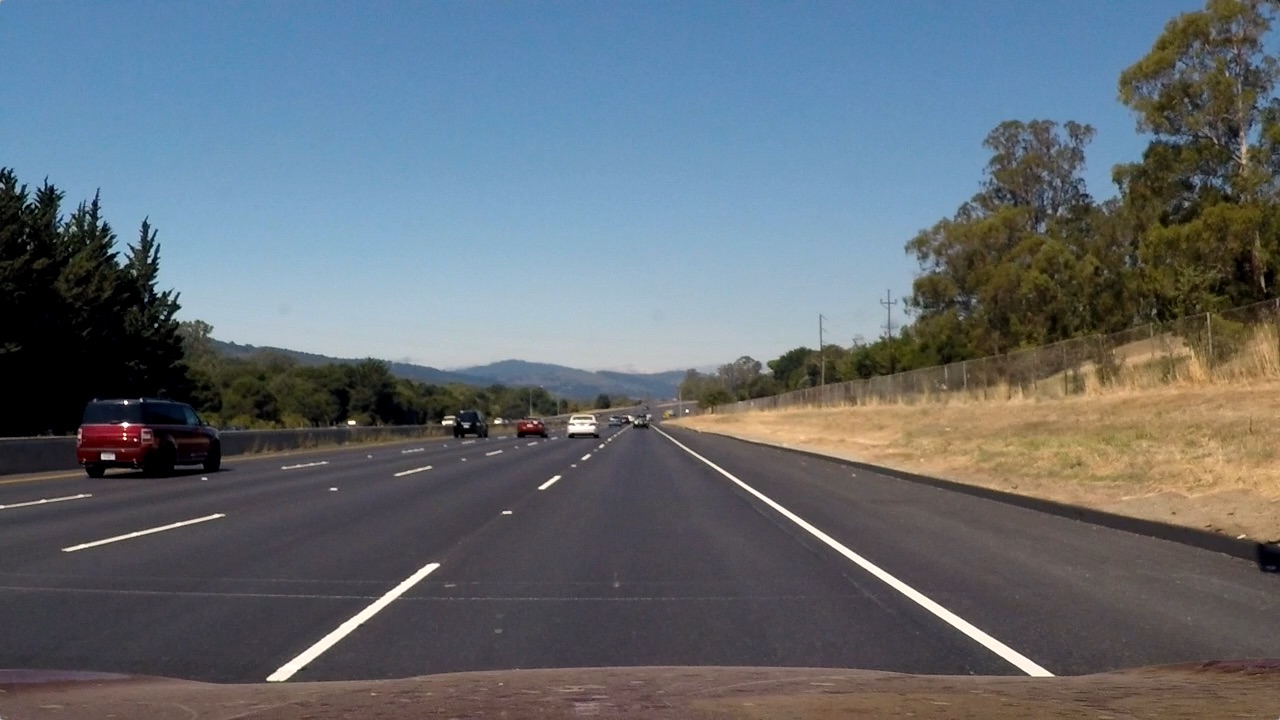

Extract its region of interest:

It is possible to transform the image into Bird’s Eye View with two different approaches:
a) stretch the top row of pixels while keeping the bottom row unchanged:
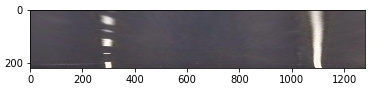
b) shrinking the bottom of the image while keeping the top row unchanged;
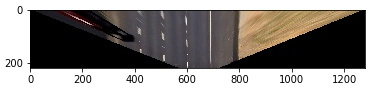
One may consider the first variant more obvious. However, it increases the spatial resolution (without adding information) for the distant part of the image and it could lead to line bounds erosion, hence, gradient algorithms may have difficulties with its detection. It also reduce viewing angle, therefore it is impossible to track other than central lanes.
The second way of transformation was selected as a better one because it preserves all avalable pixels from the raw image on the top edge where there is lower relative resolution. To find correct transformation, source and destinations points a test image with flat and straight road can be used for perspective measurements.
Code implementation with OpenCV
The whole code is quite simple:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
IMAGE_H = 223
IMAGE_W = 1280
src = np.float32([[0, IMAGE_H], [1207, IMAGE_H], [0, 0], [IMAGE_W, 0]])
dst = np.float32([[569, IMAGE_H], [711, IMAGE_H], [0, 0], [IMAGE_W, 0]])
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(src, dst) # The transformation matrix
Minv = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(dst, src) # Inverse transformation
img = cv2.imread('./test_img.jpg') # Read the test img
img = img[450:(450+IMAGE_H), 0:IMAGE_W] # Apply np slicing for ROI crop
warped_img = cv2.warpPerspective(img, M, (IMAGE_W, IMAGE_H)) # Image warping
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(warped_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)) # Show results
plt.show()Inverse transformation can be done with cv2.warpPerspective with Minv matrix, which was constracted in the same to M way, but with src and dst point swapped.
img_inv = cv2.warpPerspective(warped_img, Minv, (IMAGE_W, IMAGE_H)) # Inverse transformationThe code was used in the Lane Lines Detection project.